Oceania - What is Oceania?

Oceania – What is Oceania?
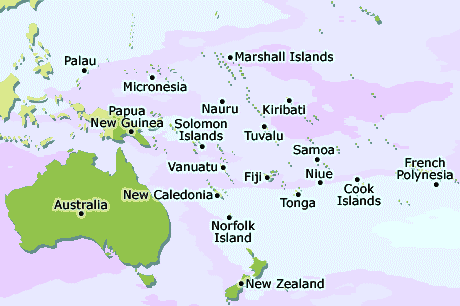
Broadly speaking, Oceania describes the region centred on all islands of the tropical Pacific Ocean, which are situated south of the Equator. There are many, many islands, both large and small that make up the “continent” of Oceania. The general regions that make up Oceania are Australia and New Zealand (termed Australasia), Melanesia, Polynesia, Micronesia and Southeast Asia.
A further breakdown of these regions is as follows - Melanesia consists of Fiji, part of Indonesia, New Caledonia (France), Papua New Guinea, the Solomon Islands, and Vanuatu.
Micronesia consists of the Federated States of Micronesia, Guam (USA), Kiribati, the Marshall Islands, the Northern Marshall Islands (USA), Nauru, Palau, and Wake Island (USA).
Polynesia consists of American Samoa (USA), the Chatham Islands (UK), the Cook Islands (UK), Easter Island (Chile), French Polynesia (France), Hawaii (USA), the Loyalty Islands (France), Niue (NZ), the Pitcairn Islands (UK), Samoa, Tokelau, Tonga, Tuvalu, and Wallis and Futuna (France)
Altogether, the population of Oceania is about 36 million, with all but 11 million living in Australia or New Zealand.
Interestingly the regions of Oceania were not colonised until the late 18th and early 19th centuries, when in contrast Europe and the America’s were colonised during the 17th Century and before.
The “continent” of Oceania is made up of Sovereign States and Dependent Territories.
Generally speaking Sovereign States have a political organization with a centralized government that has supreme independent authority over a geographic area, where a Dependent Territory is a territory that does not possess full political independence or sovereignty as a sovereign state yet remains politically outside of the controlling state's integral area.
Here is a listing of all Sovereign States and Dependent Territories of Oceania
Sovereign States of Oceania are:
The Commonwealth of Australia
Republic of Fiji
Republic of Kiribati
Republic of the Marshall Islands
Federated States of Micronesia / Micronesia
Republic of Nauru
New Zealand
Republic of Palau
Independent State of Papua New Guinea
Independent State of Samoa
Solomon Islands Kingdom of Tonga
Tuvalu Republic of Vanuatu
Dependent Territories of Oceania are:
Territory of American Samoa which is an Insular area of the United States Territory of Ashmore and Cartier Islands Territory of Australia Baker Island which is a United States Minor Outlying Island
Clipperton Island which is a French state private property
Cook Islands which are Self-governing state in free association with New Zealand
Coral Sea Islands Territory Territory of Australia
French Polynesia which is an Overseas country of France
Territory of Guam which is an Insular area of the United States Howland Island which is a United States Minor Outlying Island
Jarvis Island which is a United States Minor Outlying Island
Johnston Atoll which is a United States Minor Outlying Island
Kingman Reef which is a United States Minor Outlying Island
Midway Islands which are United States Minor Outlying Island
New Caledonia which is known as Territory of New Caledonia and Dependencies Sui generis collectively of France
Niue which is a Self-governing state in free association with New Zealand Norfolk Island which is a Self-governing integral Territory of Australia Northern Mariana Islands which is an Insular area of the United States Pitcairn Islands which includes Pitcairn, Henderson, Dulcie, and Oeno Islands are a British overseas territory
Tokelau which is a Dependent territory of New Zealand
Wake Island which is a United States Minor Outlying Island
Wallis and Futuna which are considered Overseas collectively of France
Broadly speaking, Oceania describes the region centred on all islands of the tropical Pacific Ocean, which are situated south of the Equator. There are many, many islands, both large and small that make up the “continent” of Oceania. The general regions that make up Oceania are Australia and New Zealand (termed Australasia), Melanesia, Polynesia, Micronesia and Southeast Asia.
A further breakdown of these regions is as follows - Melanesia consists of Fiji, part of Indonesia, New Caledonia (France), Papua New Guinea, the Solomon Islands, and Vanuatu.
Micronesia consists of the Federated States of Micronesia, Guam (USA), Kiribati, the Marshall Islands, the Northern Marshall Islands (USA), Nauru, Palau, and Wake Island (USA).
Polynesia consists of American Samoa (USA), the Chatham Islands (UK), the Cook Islands (UK), Easter Island (Chile), French Polynesia (France), Hawaii (USA), the Loyalty Islands (France), Niue (NZ), the Pitcairn Islands (UK), Samoa, Tokelau, Tonga, Tuvalu, and Wallis and Futuna (France)
Altogether, the population of Oceania is about 36 million, with all but 11 million living in Australia or New Zealand.
Interestingly the regions of Oceania were not colonised until the late 18th and early 19th centuries, when in contrast Europe and the America’s were colonised during the 17th Century and before.
The “continent” of Oceania is made up of Sovereign States and Dependent Territories.
Generally speaking Sovereign States have a political organization with a centralized government that has supreme independent authority over a geographic area, where a Dependent Territory is a territory that does not possess full political independence or sovereignty as a sovereign state yet remains politically outside of the controlling state's integral area.
Here is a listing of all Sovereign States and Dependent Territories of Oceania
Sovereign States of Oceania are:
Dependent Territories of Oceania are:

Related Articles
Editor's Picks Articles
Top Ten Articles
Previous Features
Site Map
Content copyright © 2023 by Judie Bellingham. All rights reserved.
This content was written by Judie Bellingham. If you wish to use this content in any manner, you need written permission. Contact Judie Bellingham for details.